Preflight Considerations:
- avoid bright white lights for at least 30 minutes prior to flight
- Requirements:
- lighted position lights
- aircraft has to be clearly illuminated
- aircraft has lighted position light
- aircraft is in an area that is marked by obstruction lights
- aircraft must have lighted anti collision lights
Check for all those lights in addition to the landing lights, taxi lights, internal and panel lights.
Brin 2 small flash light and the dim the interior panel light to maximize the night vision.
During night flight:
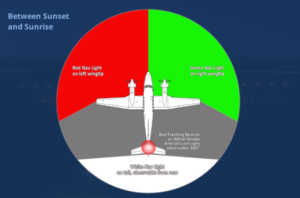
- when an airplane crosses in front of you right to left you will see a red light
- when an airplane crosses in front of you left to right you will see a green light
- when an airplane is flying away from you you will see a steady white light
- If an airplane is approaching you head on you will see a red light on your right and a green light on your left
- An aircraft that shows no relative motion with respect to your aircraft, staying in one scan quadrant, may be on a collision course. If it increase in size take evasive action immediately.
Use your 6 packs instrument more than usual.
If the tower is closed you communicate on the CTAF as you would at non towered airports.
Night flight is the same as day flight
Beware of illusions that you might be too high or too low but attempt to make takeoffs and landings as the same you would on daytime
Most midair collisions occur during clear daytime
Use flight following during night flight operations
VFR Night Fuel Minimums – Enough fuel to fly to the airport of intended landing and after that fly for an additional 45 minutes.
Civilian airport beacon flashes white and green, and know where the on the field the beacon is and you can look it up on the airport diagram with a star.
Light settings by keying the mic on airport frequencies:
- 7 times in 5 seconds (highest intensity)
- 5 time in 5 seconds (medium intensity)
- 3 times in 5 seconds (lowest intensity)
Anatomy of the eye:
Light enter the pupil which is defined by the iris, the iris expand and contract the opening to determine the amount of light in the system focusing. Behind the iris is the lens, The lens changes shape as necessary to allow focus for a sharp image on the rear part membrane which is called the retina made of photosensitive cells rods (used in low light) and cones (used in high lighting) and it signal to the brain via the optic nerve. The Fovea is just above the retina and is highly concentrated in cones.
We can look sightly to the side of an object to better see, so always look off center.
Keep your eyes moving and trust your instruments to avoid autokinesis.
At night use attitude indicator to determine wing level flight to avoid false horizon by bright light on the ground.
Tendency to fly too low (featureless terrain, dim lights)
Tendency to fly too high (bright lights steep terrain wide runway)